Methods for Quantum Simulation
Quantum simulation is among the most promising frontiers of quantum computing. We aim to design methods that lead to practical applications on current and near-term quantum devices.
Ancilla-free phase measurement of complex quantum amplitudes
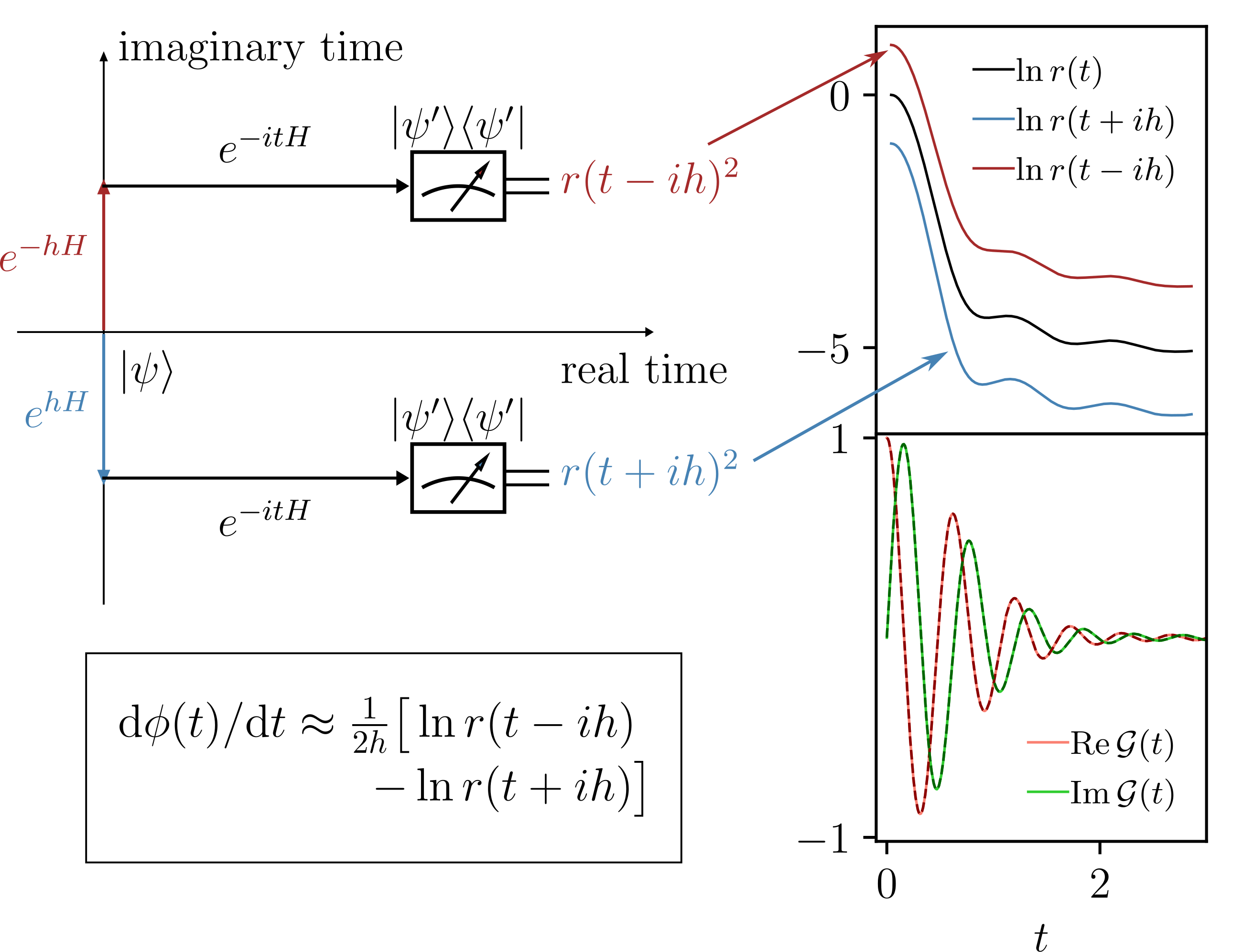
- Phase-Sensitive Quantum Measurement without Controlled Operations
Y. Yang, A. Christianen, M. C. Bañuls, D. S. Wild, and J. I. Cirac,
Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 220601 (2024)
The Loschmidt amplitude, a complex number of the form \( \langle \psi' | e^{-iHt} |\psi \rangle \), occurs naturally in various quantum algorithms, study of quantum chaos, and so on. Compared with its absolute value, the complex phase is relatively hard to extract on quantum computers. The standard method is the Hadamard test, which gives rise to large overheads due to the need for global controlled-unitary operations. We introduce a quantum algorithm based on complex analysis that overcomes this problem: no ancillary qubits, no control operations, only time evolution required.
Error-mitigated digital quantum simulation of thermalization
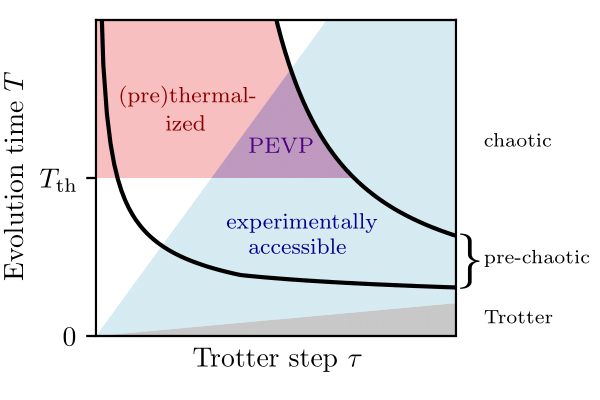
- Simulating Prethermalization Using Near-Term Quantum Computers
Y. Yang, A. Christianen, S. Coll-Vinent, V. Smelyanskiy, M. C. Bañuls, T. E. O′Brien, D. S. Wild, and J. I. Cirac,
PRX Quantum 4, 030320 (2023)
Due to decoherence and noise in current devices, it is currently challenging to perform digital quantum simulation in a regime that is intractable with classical computers. In this work, we propose a practical experimental protocol for probing dynamics and equilibrium properties on near-term digital quantum computers, based on the prethermalization phenomenon and a proposed error mitigation scheme.